"Fanm pa dra."
Women are not bed sheets.
-Haitian proverb
Las Cahobas (Kreyol: Laskawobas) is situated in the Central Plateau of Haiti. Both the Las Cahobas and the Senador rivers run through it. It is the principal city in the Las Cahobas Arrondissement. The city is noted for its proximity to the Dominican border and the Lac de Péligre, as well as its relaxed, friendly inhabitants. Approximately 10,000 people live in the center while the commune had a 2015 population of over 45,000 inhabitants.
Patronal Feast

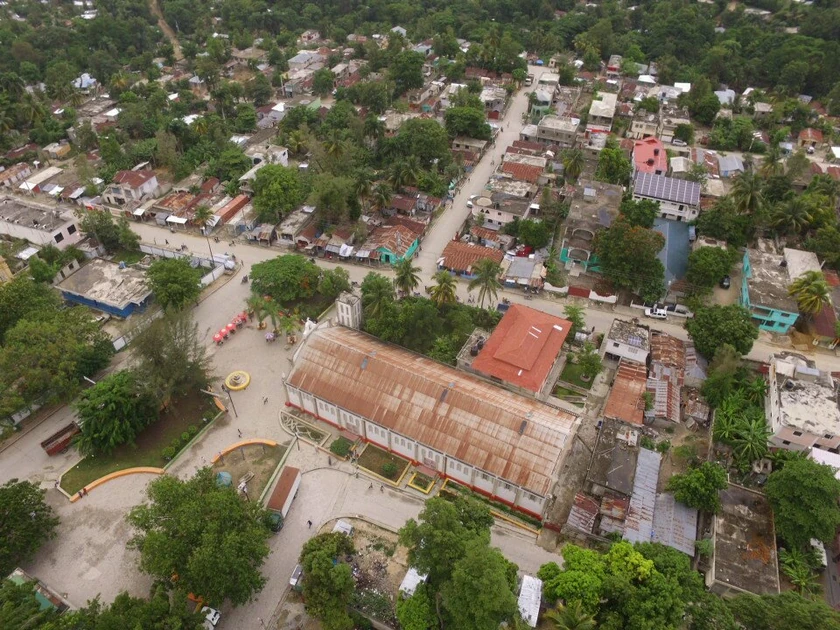
Location in Haiti
History[]
Overview
The history of the commune was marked by a particular event during the year 1808. General Henry Christophe seized the commune of Lascahobas as well as other communes such as Hinche, Saint Raphaël, and Saint-Michel-de-l'Atalaye. The Haitians kept control of this constituency for 53 years. However in 1862, the cabinet of Madrid claimed from the Haitian Government the restitution of Lascahobas and the other communes. Haiti won its case by virtue of the acquired right of prescription, a kind of uninterrupted enjoyment for more than half a century. The municipality of Lascahobas is also known for its participation in some political events. In January 1896, it took part in the general insurrection of the Cacos against Salnave.
History[]
The area of Las Cahobas was first called Les Acacjoux (meaning "The Mahoganies") by the Indian tribes which once lived there. It is located at the bottom of a narrow valley, on the right bank of a river. Its establishment dates from the Spanish government in 1760. The roofs of the small houses covered in spots or palm kernels have a worn color which makes them look like their parent town; after all, it was an annex to Bánica. It was granted municipal status in 1814. The commune of Lascahobas, which at the time was part of the Dominican Republic, received this name because of the mahogany trees that abounded in the region. This name, which translates into Spanish as "Cahobas", is the origin of the current name of the town.
By the treaty of Aranguez concluded in 1777 between France and Spain, it had become a military post placed on the limits of the two French and Spanish territories. During the revolution of 1789, many colonists who served the King of Spain to regain possession of their property, took refuge there.
• In 1808 General Christophe conquered this territory from the French expelled from Haiti in 1814, still masters of Santo Domingo. From then on, the village depended on the district of Mirebalais because of the large number of citizens of the West who settled there. The inhabitants having progressively increased, the Haitian government made it a military district and a commune provided with all public officials required by the administrative service.
• The treaty of 1814 restored to Spain the colony from which it had rid itself in 1795, and the court of Madrid did not, once again, make the least complaint.
• In 1821, the Dominicans conquered their independence and afterwards, they incorporated themselves into the Republic of Haiti. The union of the two small peoples subsisted until 1844, when the Dominicans, once again independent, never thought, even in time of war, of taking force or reelecting the territories occupied in 1808 by Christophe from the Haitian government.
Middle history
• In 1855, the Spaniards finally formally renounced their rights to Santo Domingo, officially recognizing the Dominican Republic as a sovereign state.
These were the elements of the lawsuit brought in 1862 by the cabinet of Madrid against that of Port-au-Prince, which was rightly suspected of having a negative view of the eastern homeland occupied by the Spaniards.
There was an acquired right of prescription in favor of Haiti. And at this time of 1862 an uninterrupted enjoyment of more than half a century was justified by the absence of any claim neither of Spain nor of the Dominicans and of the configuration of the place.
In 1862, Spain had just recovered its former colony; but it had not returned there purely and simply to replace the Dominican Republic, over which it held all its rights. It could only claim the territory occupied by the Dominicans since their separation from the Republic of Haiti in 1844.

Map of Lascahobas central area
About[]
Located 80 kilometers (50 miles) from the bottom of Route 3, Lascahobas (Les Acajoux by its Indian name) has remained a pleasant town despite the infrastructure challenges it faces like electricity and wastewater drainage. Spanning 150 square kilometers, it has three communal sections generously stocked with historic and tourist sites. The English forts, like Cerecite and Jacques, although abandoned today, provide information on the post-1804 defensive strategy which consisted in the creation and fortification of interior cities with a view to the eventual return of the French colonists. In terms of tourism, the Nan Remi cave, in the locality of Poulie, Nan Kafe, Nan Frechè and la Comb - a magnificent source, five minutes by car from the city center - are all assets that make Lascahobas one of the little-known pearls of Haiti.
Far from the chaotic energy that prevails in the capital, this bowl-shaped city is an oasis crossed by five rivers that offer peace of mind. Jealously protected by thousand-year-old trees, Lascahobas has survived the poachers' furia. Baited by easy money, the vultures have thrown themselves on its precious mahogany trees, either to transform them into charcoal or to sell them in the form of boards. With several adjoining streets, the city center is crossed by a road which leads to Belladère, a town bordering on the Haitian-Dominican border. Lascahobas, one of the favorite crossing points of president Jean Pierre Boyer who ruled the whole island for 21 years, is a place of ethnic mixing. At every street corner, one comes across Métis children, the fruit of stealthy copulations of the inhabitants of the two communities. Also, the Amerindian morphology of peasant women from Jumpas and Ti Fon testifies to the presence of the descendants of the first masters, of the first occupants of the land of Haiti.
At nightfall, Lascahobas is on the hush. There is no electricity or distraction. Children are often confined to their homes. But for those who come from the chaos of the capital, the chirping of birds, the fresh air, the starry sky fill with happiness, with serenity. A known pleasure, therefore not exotic for Lascahobassiens.
But also a place to exploit in the perspective of the development of ecological and cultural tourism ...Lascahobas is a small pleasure to be offered.
Geography[]
According to the IHSI, the commune has a total land area of 151.68 square kilometers (58.56 square miles), of which 69.72 km² (46%) is rural, 81.11 km² (53%) is suburban, and 0.85 km² (1%) is urban. It is bordered on the north by the towns of Boucan-Carré and Thomonde, on the east by the border town of Belladère, on the south by the town of Savanette, and on the west by the city of Mirebalais.
Lascahobas is an interior city with two communal sections. The terrain consists primarily of plateaus in one of its sections and mountains in the other. The climate of the commune is classified as tropical savannah. In the winter, there is much less rainfall than in the summer. This climate is considered to be Aw according to the Köppen-Geiger climate classification. In Lascahobas, the average annual temperature is 25.3 °C (77.5°F). Precipitation here averages 1799 mm (71 inches).
Set between the Montagnes Noires and the Trou du Eau Mountain Range, Las Cahobas includes the summit of Morne Tonnerre, elevation 1,162 meters (3,812 feet) above sea level. The mountain, located within the city's 1st section, is the highest point in the Central Department.
The Lascahobas River passes by the village, and flows into the Artibonite, at the place which serves as the eastern limit to the borough of Mirebalais by a straight line which starts from the source of Boca Cachon. Lascahobas territory is very fertile, with a healthy climate, coffee, food of all kinds, tafia, cattle, concrete sugar (rapadou) leathers and mahogany, all of which are supported by the Artibonite. These products only find a outlet by going down the rivers of the Artibonite tributaries.
Demographics
Its inhabitants are called Lascahobassien and Lascahobassienne. In 2015, the gender ratio was estimated at 96 men per 100 women. Only 19% of the municipality's population resided in urban areas. The distribution of the municipality's population by major age group is as follows:
42% of its population is under 15 years old
53% of its population is aged 15-64
5% of its population is aged 65 and over.
| Year | Population | +/- |
|---|---|---|
| 1890 | 20,000 | |
| 1998 | 54,506 | +172% |
| 2005 | 37,116 | -32% |
| 2009 | 41,716 | +12% |
| 2015 | 45,873 | +10% |
The town center, valued at 0.8 km2 (a third of a square mile), has a population density of 12,236 inhabitants per km2 (13,001 inhabitants per square mile ).
Neighborhoods[]
| LAS | Las Cahobas | 45,873 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VLB | Ville de Lascahobas | 10,401 | ||
| PEF | 1ère Section Petit Fond | 15,164 | Barrière-Gaule, Bélotte, Bissainte, Blanchard, Boucan-Tache, Chapoteau, Déma, Gilbert, Gros-Morne, La Pêgne, Laurence, Loncy, Morin, Nan Cosole, Passe-Cayemites, Petit-Fond, Richard, Roche-Mulâtre, Savanne-Croix, Ti Savane, Vieux-Joupas. | |
| JPA | 2ème Section Juampas | 20,308 | Bois Miel, Bois Sèche, Brutus, Cadette, Café, Corail, Croix-d'Maryrs, Dalmas, Dos Gravier, Dos Leron, Dos Ti Bois, Dos Zaboca, F.D. Pierre-Ville, Figuier, Flande, Fleurissant, Fond-Cicile, Fonds-Bois Pin, Fort-Anglais, Gongori, Grand-Platon, Gros-Liane, Gros-Moulin, Grosse-Roche, Jacques, La Croix, Laq Coutine, Logabuen, Mare-Rouge, Mata-Pouert, Nan Baudrin, Nan Poulie, Parc Jn Parc, Ramier, Roche-Pabre, Sénador, Tibangoule, Verdun, Wampas. |
Economy[]

Central Park in Las Cahobas, Haiti
In the economic and financial infrastructure, the municipality has a hotel, four credit unions, and five restaurants. In addition, it has eight business houses, eight exchange offices and nineteen borlette banks, including gatehouses. On the other hand, it does not have a bank. The Lascahobassiens go to other municipalities to make their banking transactions.
Agriculture dominates the economy in Lascahobas. Local farmers produce coffee, sisal, tobacco, and sugar. Sold at the busy town market, the purchase of these products keeps commerce a vital force in the community. A primary reason agriculture booms in this town is the Lascahobas River, which irrigates farmland.
Trade is also a main economic activity of the commune. The municipality of Lascahobas has at least 253 commercial establishments. The majority of these establishments (221) are small shops.
Infrastructure[]
Education

Lascahobas local school
The Ministry of the National Education for Youth and Sports is represented in the municipality by a school district office. There are four preschools, 51 primary schools, and 12 secondary schools. Only eight of these establishments are public, fourteen (14) are community-based and the other 45 are private. There were also three literacy centers and six technical and vocational institutions in the commune.
In contrast, Lascahobas's school students can get on the solar-driven Internet, and also have availability of wifi at certain locations. This service has been provided to them by the Illinois Institute of Technology.
Health

Saint-Gabriel Medical Center
The Ministry of Public Health is not represented in the commune of Lascahobas. Two health centers represent the only health facilities in this commune. The Catholic Church, Saint Gabriel, operates the Lascahobas Hospital with the financial assistance of Friends of the Children of Lascahobas. Based in the U.S., it is a non-government organization dedicated to reducing high rates of starvation, illiteracy, and health problems of residents. In addition, a team of physicians, nurses, auxiliaries and health officers form the technical staff of these facilities.
Utilities

Las Cahobas River
As for water availability, five rivers and six sources have been inventoried. Apart from these water points, there are three artesian wells and some public fountains with at least six taps. Only the city area of Lascahobas is electrified. The municipality benefits from 77 hours of electricity on average per week.
Lascahobas suffers from erratic electrical service. The government rations delivery of electricity to two days a week, but in the 80s and 90s the town was on the power grid 100% of the time. From 2006 to 2009, the town experienced a complete blackout. When violent protests broke out, the government turned the power back on.
Administration
With regard to administrative and judicial infrastructure, the municipality has a peace court, a police station, a tax office, and an civil status office. There is also a prison.
As of December 2021

City Hall
 Rodely Carietane Balde |
 Michel Fedguer |
 Presler Jean |

Las Cahobas road

Ville de Las Cahobas
Culture[]
Religion
A total of 74 temples or churches have been inventoried in the commune. The Baptist (17) and Methodist (12) denominations hold the largest number of temples or churches inventoried in the commune. Lascahobas's population is also largely Catholic, but it also has many believers of Vodun. They frequently hold festivals throughout the year in the foothills.
Organizations
The muncipality has about 15 socio-political organizations, 5 NGOs, and three non-commercial cooperatives had their representations in the commune at the time of the inventory. In addition are eleven popular organization, six peasant groups, and three women's groups.
Communication
The municipality of Lascahobas has four telephone booths. The postal Service is non-existent. It has two radio stations, but does not have a newspaper/magazine or television station. Telephone services are provided by two (2) cyber cafes.
Heritage
The patronal feast of the town is celebrated every March 24 in honor of Saint Gabriel.
Leisure

Las Cahobas waters
For entertainment, the inhabitants of the town have a library, two spaces to practice football (soccer), three night clubs, two public squares and ten gagueres. There are also 63 peristyles.
It is said that on the crest of Morne Tonnerre, which flanks Fort d'Avezac, the carcass of a ship can be found. But this has not been verified.
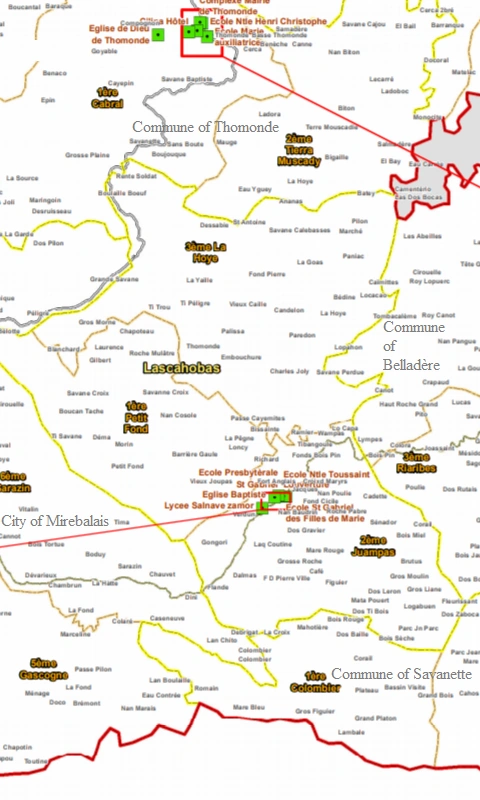
Las Cahobas local map
References[]
Lascahobas - un petit plaisir [1]
FENAMH [2]
Lascahobas [3]
Commune de Lascahobas [4]
Michael Vedrine












