
Pointe Aboury, Grand-Anse, Haiti
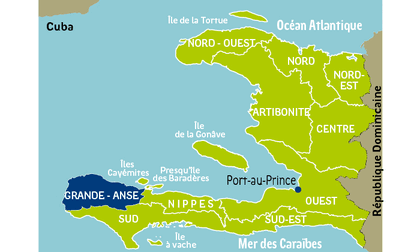
Location in Haiti. Grande-Anse Department highlighted in blue

Grand-Anse Departmental Flag
Michael Vedrine
Grand'Anse is one of the ten departments of Haiti. It has an area of 3,310 km² and a population of 733,200 (2002). Its capital is Jérémie.
Exterior boundaries
North: Caribbean Sea
East: Nippes Department
South: Southern Department
West: Strait of Jamaica
Interior boundaries
The department is divided in 3 arrondissements:
Grand-Anse main cities[]
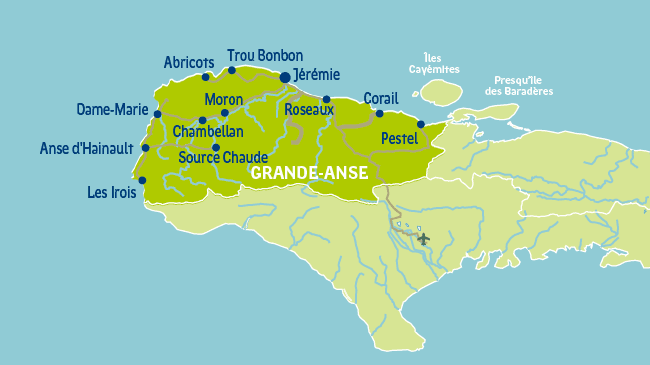
Main cities of Grand-Anse, Haiti
Grand-Anse is a department located on the northwestern end of Haiti's Tiburon Peninsula, occupying a large part of it. It is bordered by the Southern Department to the south, the Jamaica Channel to the west, Gulf of Gonâve to the north, and the Nippes Department to the east. Grand-Anse is the 3rd smallest Haitian department by area, density and population. The capital and largest city is Jérémie.
Grand-Anse became a department following 1962, when it was split from the Southern Department. The Department was further reduced with the creation of the Nippes Department from Miragoane and Anse-A-Veau Arrondissements. Grand-Anse is divided administratively into 18 communes, 79 communal sections, and eight districts.
History[]
The department of Grand'Anse consists of three cities founded in the 17th century, three in the 18th century, three in the 20th century and nine unspecified.
Prehistory and founding[]

Map showing the 5 prehistoric ancient kingdoms of Hispaniola
Three waves of cultural influence had swept the Antilles: first, the primitive hunting and gathering Ciboney coming probably from Florida; second, the Arawak, who were typically circum-Caribbean and came from South America; and third, the Carib, who were Tropical Forest rather than circum-Caribbean, and also came from South America. At the conquest the Ciboney occupied part of Cuba and Haiti. The Arawak held the remainder of the Greater Antilles, but they had been driven from most of the Lesser Antilles by the Carib, probably in a very recent prehistoric period.
The area which became the Department of Grand'Anse was originally the ancient kingdom of Guaccaiarima (or Guaicayarima) , and was inhabited by tribes of the Arawak language family, namely the Taíno. The word tayno or taíno, with the meaning "good" or "prudent", was mentioned by historians who wrote that the natives of Borinquén used the term to indicate that they were the "good men", as opposed to the Caribs. The Guaccaiarima were a Native American people of the southwestern peninsula of Haiti. Their historical territory roughly included the lands west of the Baradères Peninsula and the Cavaillon River. This people was marked as a cave population, from which circumstance at least the western part of the territory indicated is sometimes supposed to have been occupied by a people who preceded the Arawak, the Guanacahibes, who were also represented in western Cuba. Their origin is questionable, as they were probably different from the Arawaks.
Peter Martyr divided the Guccaiarima territory into cantons: Ayqueroa, Chaymi, Guabaqua, Habacoa, Ianaizi, Little Bainoa, Manabaxao, Navicarao, Nimaca, Taquenazabo and Zamana.
Geography[]
In terms of configuration, thirteen municipalities are bathed by the sea and five others are located in the interior. The dominant relief of the department is the plain with a very varied climate.
Its population in 1998 was 669,669 inhabitants with a density of 448.03 inhabitants / km2. The city of Jérémie, the capital of the department, is the most populated with 125,000 inhabitants, while Chambellan contains the highest density (454 inhabitants / km2) and Corail, the lowest (128 inhabitants / km2).
Infrastructure[]
In the field of education, the Ministry of National Education of Youth and Sports is represented in twelve communes. 45 kindergarten schools, 1,310 primary schools (preschool level included) and 83 secondary schools were listed in the department. In addition, there were 4,404 students with 86 kindergarten teachers, 141,878 students with 3,819 primary teachers and 17,472 students with 774 secondary teachers.
Health
With regard to health, the Ministry of Public Health is represented in only three communes. However, the department has nine hospitals, three clinics, 12 health centers, 28 dispensaries and 23 pharmacies. In addition, 43 doctors (graduates and trainees), twelve dentists (graduates and trainees), 79 nurses (graduates and trainees), 165 auxiliaries, 314 certified matrons and 246 other health workers train the medical staff in the department of health.
Utilities
With regard to water potential, the department is well equipped. It has 61 rivers, 249 springs, 23 ponds and eight lagoons.
Among the eighteen (18) communes of the department, fifteen (15) are electrified, six (6) served by the Electricity of Haiti (EDH); twelve (12) have a call center and nine (9) have a postal service. In addition, thirteen (13) radio stations and a television station were identified. There is no "Journal / Revue" in the department.
Culture[]
Religion
On the religion side, 286 Catholic churches and chapels, two Episcopal churches, 145 Baptist churches, 40 Adventist churches, 96 Pentecostal churches, 34 Churches of God, 25 Wesleyan churches, 22 Halls of Royaune (Jehovah's Witness) and 114 other churches were listed in the Department of Grand'Anse.
Organizations
With regard to political and non-governmental organizations, the Department has eighteen representations of political parties, 151 grassroots organizations, 19 non-commercial cooperatives, eighteen non-governmental organizations (NGOs) and 14 international organizations.
At the administrative level, the department has thirteen (13) functional police stations and four (4) prisons. All the communes of the department own at least a court of peace and a registry office. There were thirty-two (32) notaries and twenty-six (26) surveyors.
For the economic establishments, one finds in the department seventeen (17) hotels, one (1) pension, 37 restaurants, two (2) banks of which one is in Jérémie and the other in Miragoane, twenty (20) credit unions and twenty two (22) marketing cooperatives. In addition, for the other economic establishments, the department has three (3) gas stations, five (5) private morgues, sixteen (16) salons of beauty or hair, twelve (12) studios of photographs, three (3) ) dry cleanning and 81 markets with seven (7) slaughterhouses.
As for Culture and Leisure, the Department of Grand'Anse, like other departments of the country is quite equipped. In addition to the gâgeres (232 in total) which constitute the main places of distraction of the inhabitants of the Ghent Anse, one has counted there nine (9) libraries, one (1) museum, four (4) cinemas of system video , seven (7) theaters, eighteen (18) nigth clubs, seven (7) public places and 34 caves, sites and monuments that can be admired by visitors.
Photos from Grand-Anse
References[]
Grand Anse schools [1]
Tribal art reference [4]





