Aquin (Kreyol: Aken) is a port city and commune in the Southern Department of Haiti.


About[]
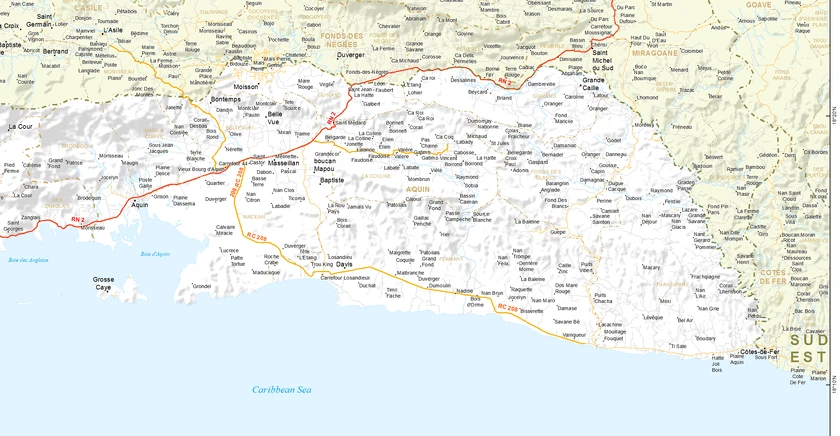
Aquin is a city in Haiti's Southern Department. It is on the Tiburon Peninsula's south shore. The population was just over 100,000 at the 2015 Census. An important center of the fishing industry and a popular summer destination, Aquin consists of an urban core towards west side of the bay, the two districts of Fond-des-Blancs and Vieux Bourg D'Aquin, and the outlying neighborhoods of Brodequin, Bellevue, Flamands, Mare-à-Coiffe, La Colline, Guirand, Frangipane, and Colline-à-Mongons.
Aquin is the largest municipality in Haiti by land area. It is the seat of Aquin Arrondissement. This quintessential Caribbean destination, nestled conveniently between Port-au-Prince and Les Cayes, is best known for its cultural diversity and strong intermingling.
Aquin has not forgotten the benefits that its former borough commander, General Dossous, has brought to its agriculture.
Aquin is located approximately 145 km (90 miles) southwest of Port-au-Prince, and 55 km (34 miles) northeast of the region known as Les Cayes.
History[]
Throughout the 15th century (1400s), the town thrived as a port city, among the most important - so important it was considered, it had been allowed the use of respective coats of arms. It continues to be an active port, but today its major industry is tourism. The town is served by Route Nationale 2 and contains Jardins Sur Mer, known locally for the best seafood in Haiti.
Aquin is also known in Haiti for its historical value as one of the country's first settlements.
Christopher Colombus docked in the port of Aquin in 1494: the natives of the area called this place Yaquimo. Alonso de Ojeda and Amerigo Vespucci also came here on September 5, 1499, after the famous expedition that took away from Columbus the honour of giving his name to the new world he had discovered. They returned in 1502, but then Amerigo Vespucci, scrambled with Ojeda, had him put in chains. The Spanish built down a town they called 'Villa nueva de Yaquimo', and which was nicknamed "Port of Brazil", because of the large amount of Brazil that was found there at the time. By 1610, this city was already abandoned by them. Around 1660, the buccaneers went there, and their pronunciation made it 'Aquin'. They then founded the village of Aquin, far from the present village of about a league and a half. This first village was located on the left bank of the Aquin River; it was transferred in 1714 to the place known today as Old Bourg, because in 1804 the Haitian government ordered its translation to the present town located at the former site of Aquin, as the project had been formed in 1768. General Borgella, then the local commander, is somehow the founder.
• Aquin gave the day to Hugues Montbrun, whose the name fills the first pages of Haiti's history. He was born on June 12, 1756 on a habitation near Aquin. He was raised in Bordeaux where he was sent at the age of 5. From captain to the regiment of the dragons of Angoulème, in 1792 became head of a battalion of national volunteers of the department of Gironde, and then moved to Santo Domingo as aide-de-camp of General Desparbès. Appointed governor general of the West, he engaged in mercantile operations in his command, which displeased the officers under his orders, ultimately resulting in unrest in Jacmel and commanded Beauvais. Montbrun accused him of being the provocative and ordered Beauvais to arrest him. As Beauvais had disobeyed this order, the soldiers of the legion who had spoken, some for Beauvais, others for Montbrun, were going to come to the hands when the officers invoked Riguad's mediation. The latter, assisted by Pinchinat, took the western command from Montbrun and entrusted him to Beauvais. After two years of detention, Montbrun was tried by a war council and acquitted by a war council. He again took up service in France, and he reached the rank of general. He died in 1831 commander of the Chateau-Trompette in Bordeaux.
• The commune of Aquin was also born Julien Raymond, a man of color, who presented in France, in 1783, memoirs to The Marshal of Castries, minister of the navy and colonies, in order to obtain equal political rights between the affranchis of Santo Domingo and the whites. This same citizen almost became the victim of Page and Brulley under the Convention, and was later a member of the Civil Commission, of which Sonthonax was the leader in 1796. An instrut and a perfect education, Raymond enjoyed a high level of consideration in all the patriotic circles of Paris. He recommended in his correspondence to the freedmen to be attached to France and the revolution, never to stand under the banners of the planters against the metropole, to follow the course of events, to claim human rights at every favorable opportunity, and to wait patiently for the time of deliverance.
• Aquin also gave birth to Piverger, a distinguished officer in Riguad's army.
• On November 26, 1789, the whites entered the house of a man named Labadie, a gens du couleur, of Aquin, gave him twenty-five gunshots, and tied him to the tail of a horse which they galloped onto a stony path. The fiery animal stopped only on the habitation of their victim, 3 leagues from the city. Labadie's family, after being insulted, cared for the torn, bloody body that miraculously escaped death. Labadie died long after this event. Because of the wisdom and purity of his manners, Labadie was called the "Venerable" throughout his township. The whites accused him of being an accomplice of Ferrand de Baudières, of Petit-Goâve.
• In 1791, Aquin's freedmen were so numerous and so powerful that the whites who lived there never dared to send deputies to the Cape colonial assembly. The freedmen shot a large number of whites in the form of lawsuits, and hanged women and infirm old men.
• In 1792, twenty-seven mulatres, caught on a boat fetching flour for the city of Aquin, were drowned.
• The Battle of Aquin (July 7, 1800) was the last civil war battle of that time. Two days after, Dessalines, after leaving the rest of his army under the orders of Brigadier General Laplume, left Aquin for Anse-à-Veau with 800 men. He took this village as well as the Petit-Trou-de-Nippes, returned to Aquin, from where he marched on Saint Louis of the South.
• When the Leclerc expedition arrived in 1802, Aquin followed the example of The Cayes: Colonel Nerette was subduing himself to the French. In December of the same year, this Nerette, a gens de couleur, had a young man of colour, Herald Charlemagne, shot in Aquin's Place-des-armes, because he had told a white man who threatened him to make him flogging, that his reign would end soon. Shortly afterwards, Ferbosse, a gens de couleur, former officer of the Toussaint-Louverture army in the civil war against Riguad, had been beaten by Léveillé, a black officer, on the Lorquet habitation, the French of Aquin accused him of treason. Although he was seriously wounded, they drowned him in the harbour. Ferbosse commanded a battalion of the 4th Colonial in Jérémie when Leclerc's Expedition arrived.
• General André Riguad, upon learning of the movement made in Aquin against the government of President Pétion, left his command of the Grande Anse and took himself to the plain of Les Cayes on October 31, 1810. More than 3,000 farmers came to surround it. Voltaire, wishing to remain faithful to Pétion was abandoned, and found himself alone in this plain with his brother Rameau. After Riguad's death, General Borgella was appointed head of the government of the South. On March 16, 1812, in Aquin, he proclaimed his submission to President Pétion.
• Citizen David Saint-Preux, a vehement speaker, one of those who were expelled from the House of Commons on August 14, 1833, represented the city of Aquin where he was born. During the revolution of 1843, David Saint-Preux was detained in Aquin's prison, from where he managed to escape to join General Riviere Hérard at Anse-à-Veau, on the march on Port-au-Prince.
• The Fodoas habitation, located in Aquin, was put up for sale by the Senate Act of November 7, 1812 for the creation of a national currency. The J.B. Anglade coffee shops and other habitations in other communes were put up for sale by law of March 10, 1814 to raise the culture and increase the number of owners.
• The first citizen to represent this commune in the first Chamber of Communes in 1817 was Baudouin, who presided over it.
• Aquin contains the remains of the generals Vaval and Francisque, former commanders of the borough.
• Aquin took up arms in 1844 against President Herard Rivière; Jacques Acao, the leader of this movement, advanced to the gates of the capital, and was stopped only by the appointment of General Guerrier as president.
• In April 1848, a conspiracy broke out in Aquin against Soulouque. Louis Jacques was the leader. Several cities in the South, like Miragoâne, where General Carrié Jr. commanded, adhered. On this news, the alarm gun was fired at Port-au-Prince on April 16. Soulouque and Similien, assisted by the Zinglins, executed a coup d'état at the national palace. Part of the entourage, bribed by Similien, fired on the generals and officials gathered in this palace: some have drowned in their blood; the others, hunted from all sides, escaped death by jumping over the gates of the garden. The chief Piquet Jean Denis took Aquin on the rebels: a hundred and eighty negres who were among them, counting that life would be left to them in consideration of their color, were garroted and slit.
• During the Cacos revolution, in 1869, Aquin was in turn attacked and taken, by the troops of the government, and also by the gangs of the revolution. General Brice surprised the Piquets by sea, in August, and cut them into pieces. Saint-Vil John, who commanded for President Salnave there, withdrew in disarray from Morne Ocro, which he abandoned shortly afterwards. He was tried, convicted and shot in Port-au-Prince for not sufficiently resisting the enemy.
• On June 2, 1883, during the Miragoâne insurrection, Aquin spoke out against the government of President Salomon, but this movement had no follow-up.

La baie d'Aquin
Geography[]
The latitude of Aquin is 18.2807° N, 73.3959° W. The legal distance of Aquin with the capital is fixed by law of April 25, 1817 to 35 leagues. According to the IHSI, the town has a total area of 638.59 square kilometers (246.56 square miles), of which 426.30 km² (67%) is rural, 208.37 km² (32%) is suburban, and 3.92 km² (1%) is urban.
With the largest land area of any municipality in Haiti, Aquin consists of several neighborhoods and geographical sections. Larger localities in the town include La Ville d'Aquin, Vieux Bourg D'Aquin, Brodequin, and Fond-des-Blancs.
Aquin's shoreline makes up the entire northern shore of Aquin Bay and straddles the Caribbean sea for over 50 kilometers (30 miles). It is bordered on land by Côtes-de-Fer to the southeast, Saint-Louis-du-Sud to the west, Miragoâne to the north and east, and L'Asile and Fonds-des-Nègres to the north. Aquin is situated in a tri-departmental area where the Sud, Nippes, and Sud-Est departments meet. This area, more specifically along Route Nationale 2 is known as "the Gate to the Southwest".
The stretch of road between Aquin and Saint-Louis-du-Sud is where the southwestern charms of Haiti really start to reveal themselves. The scenery is lush, green, and hilly, and there are long stretches where the road tracks the coast - miles of white sand beaches and the clean turquoise waters of the Caribbean Sea. It's startlingly pretty.
Aquin's border with Côtes-de-Fer makes up most of the line between Haiti's Southern and Southeastern departments.
Within the municipal boundaries is a pond called Étang Salée (Salted Pond), which is a league long and about a half mile of width: it connects with the sea via Aquin Bay.
Located in the Plaine d'Aquin, the town of Aquin has many distinct geographical features. The Hill at Mongon offers a general view of this plain, which measures 60 square km. The town's Caribbean coast is characterized by low plains, while its central and western sections are extremely hilly and forested. Aquin contains several rivers and streams flowing throughout its quadrants and on an island in the middle of one of them lie the ruins of an old English fort. A major feature of the town is the delta at la Ville d'Aquin. There is also the Riviére des Côtes-de-Fer, which forms the eastern border of Aquin and much of it's border with Miragoâne.
Aquin also has several islands off its coast such as Grosse Caye, Orange Cay, and Île des Moustiques.
Demography
| Year | Population | -/+ |
|---|---|---|
| 1890 | 12,000 | |
| 1896 | 20,000 | +66% |
| 1950 | 58,412 | +192% |
| 1998 | 68,190 | +17% |
| 2003 | 95,004 | +39% |
| 2009 | 94,773 | -1% |
| 2015 | 104,216 | +10% |
Neighborhoods
Aquin has 12 communal sections and two districts.
| AQN | Aquin | 104,216 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| VAQ | Ville d'Aquin | 9,192 | |
| MAC | 1ère Section Macéan | 7,076 | |
| BLL | 2ème Section Bellevue | 11,958 | |
| BDQ | 3ème Section Brodequin | 6,289 | |
| FLA | 4ème Section Flamands | 5,942 | |
| MCF | 5ème Section Mare à Coiffe | 7,676 | |
| LAC | 6ème Section La Colline | 16,100 | |
| FNB | 9ème Section Fond-des-Blancs | 7,248 | |
| GRD | 10ème Section Guirand | 9,614 | |
| FRG | 11ème Section Frangipane | 11,190 | |
| CMO | 12ème Section Colline-à-Mongons | 7,276 | |
| QFD | Quartier Fond-des-Blancs | 572 | |
| QVB | Quartier Vieux Bourg D'Aquin | 4,083 |
Economy[]
Aquin is an economic and tourism center of southern Haiti. The major industry is tourism, with agriculture, trade, and finance also being primary industries. Apart from a hotel, five restaurants (one large and four small), a bank and a marketing cooperative represent the economic facilities of the commune. The Ministry of Economy and Finance (MEF), is represented in the Commune of Aquin by an office and headed by a director located at Rue Julien-Raymond.
The municipality of Aquinas is famous for its horses, sheep, oysters, truffles and oranges which are the best in the country. There is also good timber, iron, spear, tender pebble, three-word wood, latanier, acorn oak, laget or lace wood, gaïac, and brazillet. Boats are built for coasting and straw hats and salt are made to eat.
Coal deposits were found three leagues away from Aquin. The municipalities of L'Asile and Camp-Perrin are the known portions of the same coal basin. Aquin's samples show a less crumbly quality than that of the mineral fuel of Anse-à-Veau. Mr. Gros, an agent of a company formed by Mr. Holt of London], had brought a survey machine in January 1883 to study Haiti's coal mines. He had left for Aquin with Mr. Eugene Nau to examine the coal depots discovered in the South. The port of Aquin, which fills the gap between Jacmel and Les Cayes, would take a maple development under the impetus of active exploitation of these coal mines, and this industry would bring back the ease.
The port of Aquin is very flared, and ships of a certain tonnage are forced to take anchorage in the distance. Except for this inconvenience, the port is safe. Accessible only by a beautiful entrance to the south, it is guaranteed offshore winds by the rock the Diamond le Diamant which cuts the pass in half, and on which comes the effort of the blades. The mangroves that line the bay are loaded with excellent oysters that are said to be superior to all those of the country, and harvested all year round. The Diamond is at 18.13'45" north latitude, and 75.48' of western longitude.
The island of Grosse-Caye is located opposite Aquin's Bay, and the tip of Morne-Rouge is to the south. The port was opened to foreign trade by law of April 21, 1807. The law of 17 December 1808 closed it. On the claims made by General Vaval, commander of the borough, on behalf of his fellow citizens, it was again opened to foreign trade.
Market day
Saturday and Wednesday are market days when Aquin buzzes with activities. Wares are traded by people who come in large numbers to the market.
Infrastructure[]
Transportation[]

Aquin, Haiti
The National Route 2 passes through Aquin which makes the region easily accessible. National Route 2 heads towards Les Cayes and traverses through town to Port-au-Prince.
The road from Aquin to Miragoâne through the municipality of Fonds-des-Nègres, through which many travellers come to buy goods from Port-au-Prince, has historically been heavily travelled. In his government program, General Légitime proposed the creation of a railway from Miragoâne to Aquin.
The road from Aquin to Anse-à-Veau was clear.
Education[]
The Ministry of National Education for Youth and Sports is represented in the Commune of Aquin by a School Inspectorate. Six kindergarten, several primary schools and ten secondary schools have been listed in the commune. The city center has five secondary schools amongst them, there is one that contains both the primary and the secondary, it's our Lady of the sacred heart of Aquinas College. There are also six technical and vocational schools, a number of literacy centers and a graduate school.
List of higher schools:
Our Lady of the Sacred Heart of Aquinas
Lycée Pierre-Sully
St. Thomas Aquinas College
Collège Jaques-Roumain
Collège Rénovateur.
List of primary schools
Yanetty School
École MEBSH d'Aquin
Ecole Armé du Salut d'Aquin
Our Lady of the Sea school
Boys national school
Health[]
The Ministry of Public Health is not represented in the Municipality of Aquin. Four health facilities were counted in the Commune with a technical staff consisting of five doctors, one dentist, eight nurses, nineteen auxiliaries and 68 matrons.
Utilities[]
With respect to water resources, the town of Aquinas has six rivers, three springs, a pond and a lagoon. In addition, sixty single wells, 150 artesian wells, public fountains with at least fifteen taps and twenty pumps were also listed. Only the city of Aquinas is electrified, and the frequency of electric power supply is about 35 hours per week. [1]
Security[]
A police station, a civil court, a public prosecutor's office, three courts of peace and a registry office constitute the administrative and judicial infrastructures of the Commune.
Tourism[]
One of the best hotels here is Jardin Sur Mer. Some of the finest delicacies like grilled shrimps and home grown oysters are prepared tastefully and served here.
Food
This place is indeed an exquisite one. Tourists and locals visit the hotels to enjoy great food sometimes served as buffets, and scenic settings naturally created by nature. Many of the hotels have an excellent view of the sandy beaches and the Caribbean Sea.
Culture[]
Religion[]
In the area of religion, the Commune of Aquin has thirty Catholic churches (including chapels), fifteen Baptist churches, seven Adventist temples, seven Pentecostal churches, three Jehovah's Witness Kingdom Halls and 26 other churches.
The Lodges are The Intimate Reunion (Réunion Intime) and the Valley of Ebron (la Vallée d’Ebron) N°52, belonging to the Grand Orient of Haiti].
Leisure[]
Aquin has some of the most amazing beaches and overlooks the Caribbean Sea. A lot of people come here to enjoy bathing in the sun and collect sea shells and coral reefs. The shells get deposited by the tide while it regresses towards the Caribbean Sea.
As for Leisure, the Commune of Aquin has a library and three cinemas. The parish hall serves as a theater room. The sports practiced in the municipality are: football (soccer), basketball and tennis. Three night clubs operating occasionally and six gaugeres were listed in the Commune.
The Fort of Bonnet-Carré is located in the municipality.
Communication[]
The Commune has a telephone service with four telephone booths. There is no radio station, newspaper / magazine, or TV station.
The post comes from Port-au-Prince and the North and arrives via Miragoâne on Sunday evening for the same destinations.
Heritage[]
As far as cultural heritage is concerned, a cave has been listed in the 12th communal section, maintained by the people of the area and especially by the pilgrims who come there to worship and celebrate Saint Gregory.
Neighborhoods[]
| AQN | Aquin | 104,216 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VAQ | Ville d'Aquin | Urban | 9,192 | ||
| QFD | Quartier Fond-des-Blancs | Urban | 572 | ||
| QVB | Quartier Vieux Bourg D'Aquin | Urban | 4,083 | ||
| MAC | 1ère Section Macéan | Rural section | 7,076 | Baptiste, Basse-Terre, Boucan-Mapou, Calvaire-Miracle, Carrefour 44, Dabon, Duverger, Grison, Grondel, Labadie, La Rou-Pays, Lucrece, Maducaque, Masseillan, Mélinette, Nan Citron, Nan Clos, Pascal, Patte-Tortue, Plaine-Dassema, Quartier, Saint-Castor, Tête-l'Etang, Ticoma, Vieux-Bourg-d'Aquin. | |
| BLL | 2ème Section Bellevue | Rural section | 11,958 | Belle Vue, Bois Rond, Bontemps, Corail-Desbas, Dandin, Jaliette, Miran, Montclair, Nérette, Olive, Paulin, Terre-Blanche, Tête-Source, Traime. | |
| BDQ | 3ème Section Brodequin | Rural section | 6,289 | Grand-Fond, Jocelyn, Maugis, Patrice. | |
| FLA | 4ème Section Flamands | Rural section | 5,942 | Bisserette, Bois-Corail, Bois-d'Orme, Caille-Zinc, Carrefour Losandieux, Coquille, Damase, Davis, Derrière-Morne, Dos-Mare-Rouge, Duchat, Dumoulin, Duverger, Gaillac-Penché, Grand-Fond, Hier, Jamais Vu, Jocelyn, La Baleine, Lacachine, Lagon-Laborieux, Losandieu, Maigrette, Malbranche, Nadine, Nan Brun, Nan Felix, Nan Maro, Nan Trompe, Passe-Campeche, Patoilais, Puits-Vibert, Raquette, Roche-Crabe, Savane Bé, Source-Blanche, Timil-Fache, Trou-King, Vainqueur. | |
| MCF | 5ème Section Mare à Coiffe | Rural | 7,676 | Nan Contrée, Plaine-Délice, Poste-Gaille, Sous-Jean-Jacques. | |
| LAC | 6ème Section La Colline | Rural | 16,100 | Bassin-Caiman, Belgarde, Boirond, Bonnefi, Cabosse, Ca Coq, Cajoux, Ca Roi, Corail, Croix-Paul, Dumornay, Elien, Faudoise, Gatimo, Grandécor, Jonette, Labady, Labate, La Colline, La Hatte, Lalanne, Michaud, Mombrun, Pas-de-Chaine, Patoilais, Raymond, Saint-Médard, Sobia, Valère, Vièle, Vincent. | |
| FNB | 9ème Section Fond-des-Blancs | Rural section | 7,248 | Adonis, Anglade, Balangrin, Bellegarde, Bernadel, Cacique, Camilet, Ca Pin, Colas, Damagnac, Damaniac, Dugué, Fond des Blancs, Fraicheur, Gaspard, Guêpe, Nabonne, Oranger, Périne, Savane-Sainton, St-Jules. | |
| GRD | 10ème Section Guirand | Rural | 9,614 | Beucard, Blaise, Briand, Ca Roi, Caroline, Dembreville, Dessalines, Fond-Maricile, Latour, Lohier, Oranger, Plaine-Abraham. | |
| FRG | 11ème Section Frangipane | Rural | 11,190 | Bel-Air, Boudary, Corail-Lhérisson, Cotes-de-Fer, Danneau, Dubois, Ferdile, Frachipagne, Godet, Gousse, Grande-Passe, Grande-Savane, Hatte-Joli-Bois, Lazare, Lévêque, Macary, Mascary, Méxi, Morency, Mouillage-Fouquet, Nan Déjour, Nan Gerard, Nan Glacis, Nan Grié, Nan l'Air, Nan Perdu, Plaine-Aquin, Pommier, Puits-Chacha, Raymond, Ti Salé. | |
| CMO | 12ème Section Colline-à-Mongons | Rural | 7,276 | Bidouze, Faubert, Galbert, Genne, La Hatte, Mare-Rouge, Moisson, Saint-Jean, Virgile. |
References/Links[]
[www.stratfordbeaconherald.com/2018/02/08/londoner-john-eberhard-sheds-light-on-haiti-rotarian-project-to-stratford-club] - Lending Haiti a helping hand Michael Vedrine